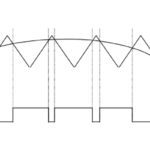
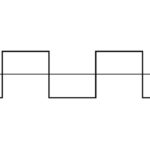
The basic function of a servo drive is to convert, or amplify, low-power signals from the controller into higher-power signals to be delivered to the motor windings. Servo drives (also referred to as servo amplifiers) can be either linear or switching types, depending on how power is delivered to the motor from the switching devices […]
FAQs + basics
When is dither helpful in motion control systems?
Dither is one of several terms used to describe small, rapid, back-and-forth movements of an object. Depending on the context, when the term “dither” is used in motion control systems, it can refer to purposeful, commanded movements or to unintended, unwanted motion. In some motion systems, dither is purposely induced to reduce the effects of […]
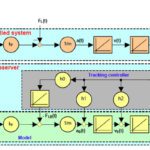
What is an observer in motion control and how does it affect performance?
A servo control loop uses sensor feedback to determine whether the system’s actual state (position, velocity, or torque) matches the commanded state. But sensors feedback isn’t perfect — even high-quality encoders and sensors can introduce noise, phase lag, and other errors in measurement. One way to improve the feedback of a servo control system is […]
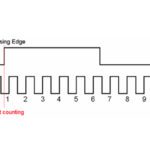
What type of encoder can measure speed?
Encoders and resolvers are used to track the angular or linear position of an object, such as a motor shaft (angular measurement) or a linear actuator (linear measurement). And with the addition of a clock signal, encoders and resolvers can also be used to measure the speed of the object. A resolver uses a rotor with […]
What’s the difference between radial and axial ring encoders?
A traditional rotary encoder measures the position or speed of a rotating shaft, with mounting via a coupling or a hollow bore that allows the encoder to fit over the shaft. But not all rotating components have a shaft to which the encoder can mount. For example, direct-drive rotary motors — also known as torque motors, […]
What are Sawyer motors and where are they used?
Originally named for Bruce Sawyer, who patented the design in 1968, Sawyer motors are a type of planar motor, and are sometimes referred to as “dual-axis linear stepper motors” since they use stepper motor technology and the moving part can travel in both the X and Y directions. Like other planar motor designs, Sawyer motors […]
Updated MEPS: Regulation (EU) 2019/1781 for motors and drives takes effect in July 2021
In 2011, the EU implemented minimum efficiency performance standards (MEPS) for electric motors used in residential, commercial, and industrial applications with Commission Regulation (EC) 640/2009, which was implemented in three stages through 2017, and its amendment Regulation (EU) 4/2014. In October 2019, Regulation (EC) 640/2009 was replaced with Commission Regulation (EU) 2019/1781, which outlines updated efficiency […]
What are electromagnetic power-off brakes and where are they used?
Power-off brakes are commonly used in motion control applications for stopping or holding a load (or both), especially on vertical axes or for emergency stop functionality in servo applications. Power-off brakes are so named because the brake is engaged when power is removed from the system — either intentionally or accidentally. (Power-off brakes are also […]
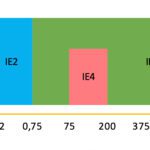
What is Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) and how is it used in industrial applications?
Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) is a technology that provides Ethernet transmission over a single pair of copper wires, while also transmitting power to connected devices via Power over Data Line (PoDL). Single Pair Ethernet was initially developed to meet the demands of the automotive industry — smaller, lighter cables and connectors for transmitting data from […]
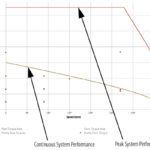
How to calculate continuous and peak torque values for servo applications
One of the most important tools for sizing a servo motor is the motor’s torque-speed curve, which shows the combinations of torque and speed that the motor can produce in two operating zones — continuous operation and peak, or intermittent, operation. To prevent thermal overload of the motor — and the drive — it’s important to […]