A common function of a conveyer system is to accumulate products — in other words, to stop them from moving along the conveyor to create a buffer, establish a queue, or smooth out differences in material movement between upstream and downstream operations. But traditional accumulation methods allow products to bump into each other and stack up […]
FAQs + basics
Micro motors give robotic hand a boost
Among the changes to small motor design over the years has been the use of powerful rare-earth magnets to increase power density, making for smaller and more powerful motors. These motors are finding their way into medical devices, robotics, as well as the intersection of these two. Case in point; a robotic glove. Ironhand from […]
Sensors aid packaging machine flexibility
Sensors have always been the unseen elements that make complex machines perform at their optimal level. This is true for all kinds of machines, including the latest generation of packaging machines. Companies that need to invest in packaging machines value flexibility where a single machine can handle a wide range of package sizes and formats. […]
What are geared cam limit switches?
Electromechanical switches are often placed at the ends of linear axes to indicate the limits of travel. But for applications with rotary — rather than linear — motion, geared cam limit switches can perform a similar function by tracking rotations of the motor shaft and triggering switches to stop movement when the specified number of […]
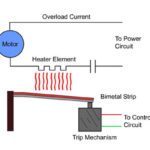
What are thermal overload relays and what motion components do they protect?
Heat is a major factor in the performance and life of a motor, and one of the primary sources of motor heating is current running through the motor windings. Since heating is an unavoidable condition of motor operation, it’s important to protect the motor from overheating, or thermal overload. In a previous post, we described […]
What are HMI-PLC combination units and where do they make sense?
PLCs have long been an industry standard in machine control. They range in size and function from the simplest of controllers with the most basic ladder logic instruction set to multi-function complex units that can provide multiple control modes from basic control functions to process control and even motion control functions. (Programmable automation controllers, or […]
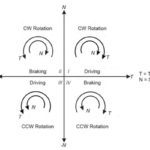
What’s the difference between dynamic braking and regenerative braking?
When a motor’s rotor speed is greater than its synchronous, or designated, speed, it can act as a generator, creating electrical energy from mechanical energy. This electrical energy needs somewhere to go, and there are two ways to deal with it — dissipate it as heat, or reuse it. Dynamic braking takes the energy generated […]
What are busbars and how are they used in motion control applications?
Busbars are components that facilitate the distribution of power to electrical equipment, supplementing or replacing traditional wiring in applications such as commercial facilities, data centers, and industrial plants. At their most basic, busbars are relatively simple bars, strips, or rods made of copper, brass, or aluminum, but in many cases, they’re constructed in specific shapes […]
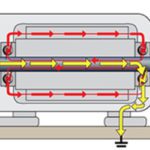
What are bearing currents and what causes them?
Pulse-width modulation is a fundamental operating principle of variable frequency drives (VFDs), but the high-frequency switching that delivers pulses of voltage from the drive to the motor can cause bearing currents — high-frequency currents that flow through the motor bearings, often leading to damage and premature failure. To achieve pulse-width modulation, insulated gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs) […]
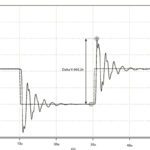
What is cable ringing between AC drives and motors and how can it be avoided?
Variable frequency drives use a technique referred to as pulse-width modulation (PWM) to provide voltage of varying frequency to an AC induction motor. The inverter, or output, stage of the VFD uses insulated gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs) that switch on-and-off rapidly, creating trapezoidal pulses of varying width to simulate AC sinusoidal voltage. But the windings in […]