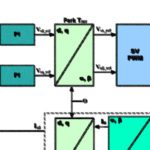
Many of the components that make up a variable frequency drive (VFD) are semiconductor components, which are sensitive to power or current surges, voltage spikes, line distortion, and general power anomalies. A line reactor is an optional component that can be added to a drive system to protect the VFD and other devices from power […]
AC Motors
What is a rectifier?
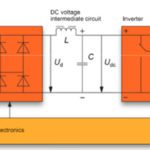
AC motors can be operated directly from AC supply voltage, but this is only suitable if the motor is required to run at constant speed. If the speed or load requirements of the motor change, an AC drive — also referred to as a variable frequency drive (VFD) — can vary the voltage and frequency […]
FAQ: What is dynamic braking and when is it used?
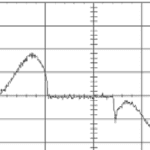
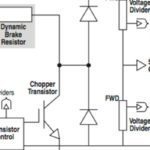
When a motor is in an overhauling condition—that is, the load is moving faster than the designated motor speed—the motor acts as a generator and produces electrical energy from mechanical energy. This electrical energy, however, needs somewhere to go, and the most common way of dealing with its release is through dynamic braking. How dynamic […]
FAQ: What are regenerative drives and where are they used?
The main purpose of a motor is to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. But when the motor’s synchronous speed is less than the rotor speed, the motor acts like a generator and converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. This energy is typically fed back into capacitors in the DC bus, but the bus can […]
FAQ: When are closed-loop and open-loop vector control useful?
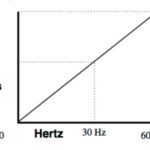
AC drives have historically been controlled by a scalar method known as volts per hertz (V/Hz), in which the drive maintains a constant voltage-to-frequency ratio in order to maintain stable torque production. However, the V/Hz control scheme doesn’t allow tight speed regulation and is limited in its ability to produce torque at low speeds. Vector […]
FAQ: What is V/Hz control mode for AC drives?
AC motors are commonly paired with variable frequency drives (VFDs), which control motor speed by regulating the frequency of the supplied voltage. Depending on the application and level of speed regulation required, VFDs can be controlled by either scalar or vector methods. The most common type of VFD control is a scalar method referred to as volts […]
Groschopp announces AC Motor-Control combo with chassis enclosures
Groschopp, Inc. is currently setting apart its AC motor-control combo by implementing strategic compatibility design measures. When matched with Groschopp motors and gearmotors, the DA1225K-0 and DA1215K-0 reduce slip and increase efficiency better than other drives on the market. In addition, these AC controls exhibit the following characteristics: Short circuit protection Input voltage options: 115/208/230 […]
Field oriented control vs. sinusoidal commutation
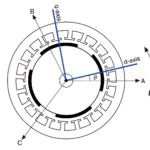
Brushless AC (BLAC) motors are driven with sinusoidal AC currents, and due to skewed magnets and sinusoidally distributed windings in their stators, they also produce sinusoidal back EMF. Sinusoidal commutation is a common way to control BLAC motors, as it provides a very consistent torque output with little torque ripple. But at high speeds, sinusoidal […]
m500-P compact three-phase AC motor for premium IE3 Efficiency Class
A leading global manufacturer of electrical and mechanical drives, motion control and automation technologies, Lenze Americas introduced the m550-P three-phase AC motor designed to achieve IE3 efficiency class in accordance with IEC60034-30 during MODEX 2016. Compared with IE2 class motors, the new Lenze motor range reduces energy lost and cost by up to 20 percent. […]
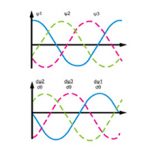
FAQ: What is sinusoidal back EMF with sinusoidal current?
Both brushless DC (BLDC) and brushless AC (BLAC) motors are permanent magnet, synchronous devices. They both produce torque and speed through the interaction of a rotating magnetic field in the stator and permanent magnets on the rotor. But while they have many similarities, differences in their stator construction produce different back EMF waveforms and result […]