When a voltage is applied to a piezoelectric material, it generates motion and force due to the expansion or contraction of the material. Piezo actuators take advantage of this effect, incorporating piezoelectric materials into useful devices for generating very small, high-frequency movements and producing relatively high forces.
Flexure guided piezo actuators incorporate mechanical hinges (flexure linkages) that amplify the motion of a stacked piezo actuator. The linkages are designed to flex (hence the term “flexure guided), and their arrangement provides motion that is perpendicular to the expansion (or, in come cases, contraction) of the piezoelectric stack. The amount of voltage applied determines the amount of motion of the piezo material, and therefore, the stroke of the actuator.
Watch a flexure guided actuator in motion.
(Video courtesy of Dynamic Materials and Structures, LLC)
While piezo materials can typically move just 0.1 – 0.2% of their length, the amplification provided by flexure guided actuators makes them suitable for travel up to several millimeters. When even longer travel lengths are needed, a lever can be incorporated into the flexure guided piezo actuator to provide a secondary level of motion amplification, producing movements up to 10 mm. Lever mechanisms have a higher response than standard flexure guided piezo actuators, due to a smaller moved mass. However, they have less stiffness than standard flexure guided designs.
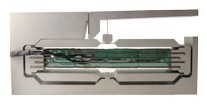
Image credit: Dynamic Structures and Materials, LLC
Despite their small size, flexure guided piezo actuators typically produce blocking forces in the hundreds of Newtons, although some designs provide forces of 1000 N or more. When used in a closed-loop system, they can achieve nanometer-level repeatability. A unique benefit of the flexure guided design is that it relies on elastic deformation rather than friction-based motion, so no lubrication or maintenance is required and lifetimes can reach several billion operating cycles.
Blocking force is the maximum force that a piezoelectric actuator can produce against a fixed load. The amount of force generated depends on the load’s stiffness. That is, the load must be stiff enough to prevent the piezo material from expanding when a voltage is applied.
Flexure guided piezo actuators provide a larger travel range in a smaller package than other piezo devices. With no lubricants or other materials that outgas, they’re suitable for vacuum applications, and their components can be made from non-magnetic materials for use in environments with strong magnetic fields. Typical applications for flexure guided piezo actuators include micro-dispensing and pumping equipment for the medical industry, atomic force microscopes, and optical inspection devices.
Feature image credit: Physik Instrumente L.P.


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.