Edited by Zak Khan || Torque margin is the amount of extra torque capacity a stepper motor has to ensure successful operation without stepper motor stalls. A sufficient torque margin is critical when a motion design incorporates stepper motors for motion, as in many cases there’s no correction of motion if the motor is temporarily overloaded.
Read FAQ: How do stepper motors handle inertia mismatch? for an explanation of the consequences of inertia mismatch and its relationship to torque.
When working with stepper motors, the rule of thumb is that a good inertia ratio between system and motor is 1:1. High-performance systems often have an inertia ratio of 3:1. Other less demanding applications can have ratios of 1:1 to 10:1 and still work well.
Stalls occur when the stepper motor is undersized relative to the load the system places on it. To prevent this, make the following calculations to identify motors up to the motion task:
• Define the motion profile. This means setting parameters such as required positioning time, acceleration and deceleration time. Also determine the positioning increments and required accuracy and resolution.
• Calculate speed, inertia of the load, holding torque, acceleration torque and load torque. Include a safety factor in these calculations.
• Select a potential motor by consulting speed-torque curves. For more information on torque curves, read FAQ: What is pullout torque and why is it a critical stepper motor value?
Remember to match the power available to the power required by the stepper motor.
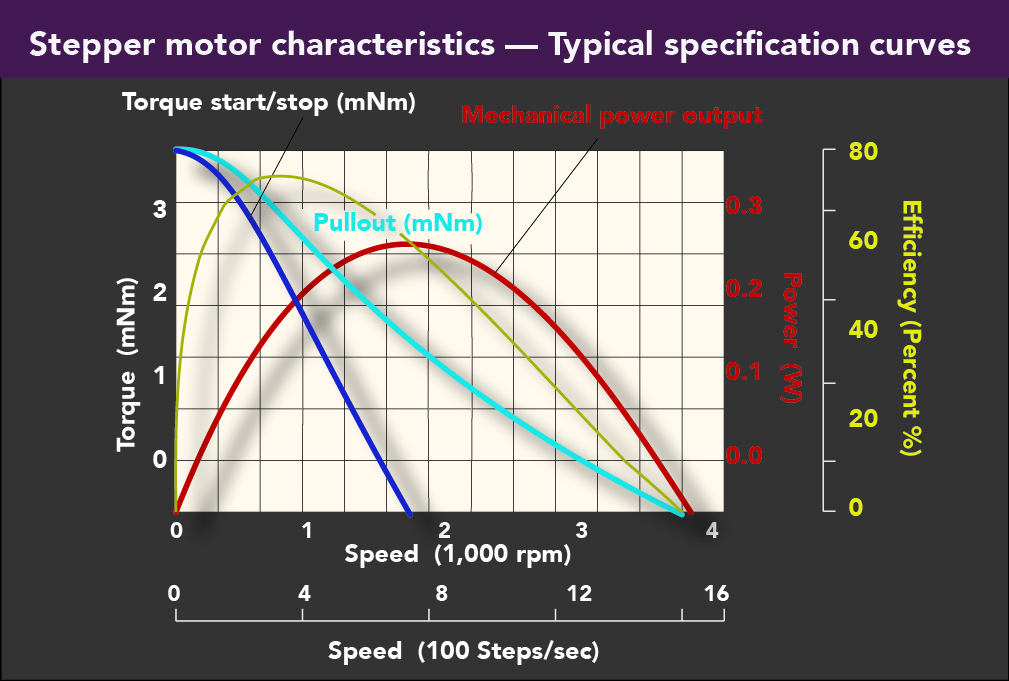
• Once the potential motors for a given application are identified, ensure the inertia ratio falls between 1:1 and 10:1 if possible — and does not exceed 20:1. Keep in mind the specifics of the system.
After performing these design calculations, also contact the manufacturers of suitable stepper motors to answer specific questions. Get all design documents for the stepper motor to check torque curves as well as the motor’s power consumption, drivers, damping and step angle.
Related FAQs about stepper motors
FAQ: What is pullout torque and why is it a critical stepper-motor value?
How to Select a Servo Motor: A Motion Engineer’s Guide
How to Select and Specify Stepper Motors: A Motion Engineer’s Guide
How to Size and Select a DC Motor: A Motion Engineer’s Guide


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.