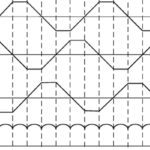
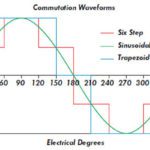
In a brushless DC (BLDC) motor, permanent magnets are mounted to the rotor, and the stator has windings that are energized by external current to produce electromagnetic poles. Brushless motors use electrical commutation to determine the switching sequence of the stator coils, and BLDC motors can be driven with either trapezoidal or sinusoidal commutation. Trapezoidal commutation is a simpler method, but it produces torque ripple at each commutation step, especially at slower speeds. Sinusoidal commutation is often used because it eliminates torque ripple and provides smooth motion, but it introduces another challenge: phase lag.
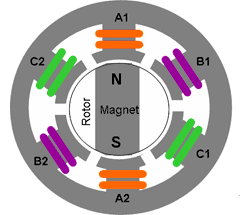
Image credit: Woodbank Communications, Ltd.
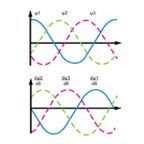
Sinusoidal commutation provides each of the motor windings with currents that vary sinusoidally as the motor turns. In order to produce maximum torque (and also eliminate torque ripple), the combination of the winding currents must produce a current vector that is constant in magnitude and orthogonal to the rotor magnetic field.
But as motor speed increases, the frequency of the sinusoidal signals increases. Back EMF, which the motor must overcome in order to maintain the required torque, also increases in both amplitude and frequency. Since motor controllers—typically PI controllers—have limited bandwidth and response, it becomes difficult for them to track the sinusoidal control signal and to overcome the increasing back EMF. The result is phase lag between the stator current vector and the rotor field.
When a coil and magnetic field rotate relative to each other, an electromotive force (voltage) is induced. In a motor, this force is referred to as back EMF, because it acts against the driving voltage and reduces current through the motor.
When the stator and current fields are no longer orthogonal, less torque is produced for a given amount of current. In other words, to maintain the same amount of torque, current must be increased. Hence, efficiency is reduced.
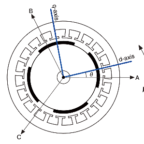
Another control method, known as field oriented control (FOC), can eliminate phase lag. In field oriented control (also referred to as vector control), the current vector—both magnitude and direction—is controlled in direct relation to the rotor, rather than on the basis of sine waves. This eliminates the phase lag between the stator current vector and the rotor magnetic field.
Feature image credit: Wikipedia


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.