Condition monitoring of machines is intimately linked with the larger program of predictive maintenance. The goal of predictive maintenance is to reduce or eliminate entirely sudden and catastrophic machine failure by actively monitoring those components that are critical to machine function. By monitoring components such as motors, fans, pumps and other constituent components such as bearings and keeping track of parameters such as temperature and vibration, and using algorithms to analyze data collected in this way, failures can be avoided before they happen.
One of the most common techniques used in condition monitoring is vibration analysis. Basically, this method uses sensors to monitor vibrations in a machine and machine components. This data is then further analyzed down stream to determine if there is a deviance from normal operation and if and what kind of intervention is needed.

Vibration sensors are widely used to measure vibration. Typical vibration sensors will measure the vibration of machine components such as shafts and bearings of rotating equipment such as motors and pumps. Vibration sensors themselves are based on several different types of operating techniques including the most common that are accelerometer based. Other vibration sensors operate using strain gages, microphones or pressure-based sensors, or other types of measurement techniques.
So, how do vibration sensors work? At the heart of the most common type of vibration sensor is an accelerometer. All accelerometers measure acceleration, which is a force. In essence it measures the degree of motion of an object. So in a sense it isn’t vibration that is directly measured but rather a force that is detected which is identified as vibration.
One of the most common types of vibration sensor uses a ceramic piezoelectric sensor or accelerometer. The accelerometer measures the dynamic acceleration of a physical object using the voltage generated from the piezoelectric effect. Basically, some materials exhibit the capacity to produce a voltage in response to a mechanical stress. These materials, or crystals, form the central part of accelerometers used in vibration sensors. So an acceleration is transmitted to a mass inside the accelerometer that then generates a proportional force on the piezoelectric crystal. This force on the crystal generates an electrical charge that’s proportional to the force, which is the acceleration.
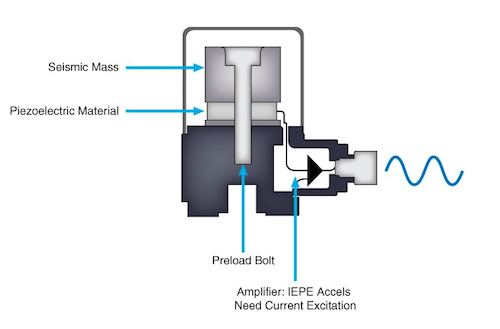
Piezoelectric-based accelerometers offer a number of benefits. For one, their high frequency response, linearity over a wide frequency range, and wide bandwidth aid in measuring high frequency vibrations. Especially in industrial applications, vibration sensors usually have a few features that ensure long-term reliable operation. These include a wide operating temperature range, a number of different packaging options, and long-term stability.
Selecting the right vibration sensor begins with understanding the expected signal characteristics to be measured and any of the environmental factors that have to be taken into account such as temperature range or hazardous environments. From this one can know the sensitivity range and frequency range needed from a sensor. The sensitivity range depends on knowing the expected vibration amplitude that the sensor is likely to encounter. Similarly, the frequency range also can be estimated or known from past frequency data from the machine or component to be monitored.




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.