When choosing a motor for an application, consider key differences between each motor’s operation.
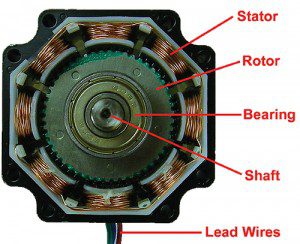
the stator, rotor, shaft, bearing and lead wires.
Stepper motors: Performance positioning
Stepper motors work for precise positioning and control with torque. Intermittent moves is what steppers output best. Tip: Don’t use stepper motors for continuous operation. When applications need motors to operate nonstop, steppers exhibit dwindling efficiency and torque.
Also read: How to select a dc motor
Stepper motors are also suitable on axes that must hold loads still for extended lengths of time, as the motors can remain in one position indefinitely. With proper design and damping, the motors can also output motion with minimal velocity ripple. Additionally, stepper motors have high repeatability and are reliable. From a cost perspective, they are often far cheaper than servomotors and can often be used in applications where servomotors are used with significant savings.
Brushed motors: Consumer designs, mobile machinery and more
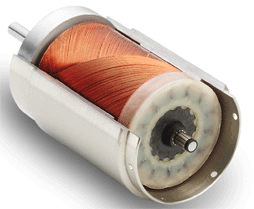
Brushed dc motors are a mature technology. Their familiarity makes them easy to use. Despite drawbacks (such as commutator and brush wear) they still have advantages. They cost less than some options, especially when OEMs buy them in bulk. A linear torque-speed relationship makes them easier to control.
Also read: Where do brush DC motors still make sense?
When designers pair them with simple speed controllers, brush motors can be useful in automotive, consumer appliances and home goods and toys.
Brushless dc motors: Efficient and durable

Brushless DC motors remove the concern of brushes and their associated wear and arcing. They are more efficient than brush motors as they have less internal friction. They usually last longer and expose the surrounding environment to less electromagnetic interference. Brushless dc motors are suitable in low-power applications (such as consumer products) as well as high-power uses (in electric vehicles and industrial machinery, for example). They are slightly more expensive than brushed DC motors.
For all of these types of motors, keep in mind voltage availability, size and torque and speed, as well as lifespan requirements.





Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.