Edited by Zak Khan || It may seem as though linear encoders and rotary encoders have strictly defined (and maybe even mutually exclusive) applications. Prevailing logic is that linear encoders track linear motion and rotary encoders track rotating shafts — but this isn’t always the case. Some motion designs can use linear or rotary encoders, […]
Linear Encoders
Ways to wire an absolute encoder into a motion system
Absolute encoders are traditionally wired in one of three ways: in parallel, with a serial interface, or over a bus. The serial and bus interfaces have multiple protocols or standards, some of which are open-source, while others are proprietary to specific manufacturers. When considering how to wire an absolute encoder, the required resolution, level of […]
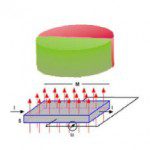
FAQ: How do magnetic encoders work?
Encoders, whether rotary or linear, absolute or incremental, typically use one of two measuring principles—optical or magnetic. While optical encoders were, in the past, the primary choice for high resolution applications, improvements in magnetic encoder technology now allow them to achieve resolutions down to one micron, competing with optical technology in many applications. Magnetic technology […]
What are capacitive encoders and where are they suitable?
Two types of encoders dominate the general industrial market—optical and magnetic. But capacitive encoders, a relatively new introduction, offer resolution comparable to optical devices, with the ruggedness of magnetic encoders. Currently, there are only a handful of vendors for capacitive encoders, but their suitability for applications requiring high precision and durability make them a good […]
FAQ: What do X1, X2, and X4 position encoding mean for incremental encoders?
An encoder is a device that measures position, and in some configurations, can also measure direction. Rotary encoders measure rotation of a shaft, while linear encoders measure distance traveled. For both types of encoder, the position measurement can be either incremental or absolute. An incremental encoder measures change in position, but does not keep track of […]
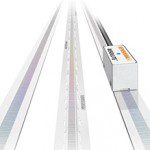
Linear encoder types — and parameters for selection
Linear encoders monitor linear movement and provide position feedback in the form of electrical signals. In servo driven systems, linear encoders supply the precise position of the load, typically in addition to the speed and direction feedback provided by the motor’s rotary encoder. For stepper driven systems, which typically operate in open-loop mode with no position […]
Programmable Encoders: The Next Generation
by Jarrod Orszulak, Product Manager, POSITAL-FRABA The latest programmable encoders offer both incremental and absolute functionality on one hardware platform and can be programmed with a WiFi connection. Programmable incremental encoders have become more common recently. This is largely due to the fact that the measurement characteristics of the device (number of pulses per rotation, […]
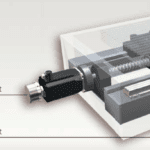
Linear motor stage with absolute encoder and ironless motor
Physik Instrumente has released a new member of the PIMag family of precision positioning stages with magnetic direct drives. The compact ultra-precise V-551 motorized linear translation stage debuted at Laser World of Photonics, held in Munich, Germany last month. V-551 comes equipped with an integrated absolute-measuring, 2nm resolution encoder – no more wasted time for […]
Tiny kit-style encoder: New option for linear measurement
A tiny linear encoder from RSF Elektronik is an MS 15 optical kit-style with the smallest mechanical profile in the industry. Available in North America through HEIDENHAIN, the encoder works in machinery for metrology, semiconductor, medical and automation. The MS 15 optical kit-style encoder is 36 x 13.5 x 14.8mm in size, and provides a 40 […]
Fagor Automation introduces Nanometer High Resolution Linear Encoders
Fagor Automation Corporation has developed and introduced a new line of Linear Encoders capable of 50 nanometer resolution. Designed for high performance markets such as precision grinders and the EDM market. In addition, due to the ability of the new product capability of achieving nanometric measurements directly from the encoder without the need for electronic […]