Edited by: Paul J. Heney, Editorial Director
Mechanical engineers often overlook important electrical issues when specifying their respective parts of an electromechanical system. This targeted advice will help you design your next electromechanical system.
Mechatronic systems are the state-of-the-art technology in automation systems, intelligently integrating mechanical and electrical elements to perform increasingly complex and demanding functions. When designing electromechanical systems, mechanical engineers and electrical engineers may tend to emphasize the technologies, components and design principles from their single area of expertise—which can lead to systems with higher operating costs, increased maintenance demands and less than optimal performance. Electrical engineers involved in helping design and build mechatronic systems often see how inefficiencies and unnecessary complexity can be unintentionally designed into machines.
Better mechatronic systems can be created when mechanical engineers consider five crucial concepts when designing manufacturing systems, to derive the greatest value and efficiency electronics systems can offer to the manufacturing process.
1. Create a clean design
Good mechatronics design starts with good mechanical design—the best electronics and electrical systems can’t compensate for poor mechanical design. The most successful designs are clean; they feature a strong, rigid frame, using materials and structural principles to ensure that, whatever motion the machine undergoes, its long-term stability is engineered-in. Make sure that rigid bearings and support are used where motors are mounted on machines; this helps prevent shafts being sheared off due to microfractures that occur because the motor shaft is mounted out of alignment with a pillow block bearing or gearbox input planetary gear.
Place motors on the machine in the best location so that operators aren’t accidentally stepping on cables and connectors causing damage, and design machine guarding with easy access points to get to motors mounted under the wing base of the machine while still protecting them against harsh environments. Most importantly, a clean design balances mass and motion: sturdy, durable framing that withstands years of vibration and shock, combined with lighter-weight components for the moving parts of the machine. This helps reduce mass, provides more energy-efficient motion, and makes it easier to size-up smaller motor/drive components for the machine. We’ve seen a lot of innovative mechanical machine designs over the years, and a clean design makes the largest contribution to a machine’s longevity, robustness, and lowest overall cost of ownership.

2. Directly couple the motor to the load
Effective mechatronics starts with a clean slate design. In the past, machines were often built around a single ac motor powering a machine line shaft, to which were attached gearboxes, pulleys, sprockets, chain drives and other mechanical devices for moving individual areas of the machine in synchronization—an approach to powering manufacturing that literally can be traced back to the dawn of the Industrial Revolution.
Consider replacing this architecture with individual servomotors coupled directly to the load you are moving. There are multiple design, machine cost and operational advantages to this solution (which a surprising number of machine designs do not use). First, consider cost: Every time you add a gearbox, you add multiple costs; it’s an additional point of failure, it has to be lubricated, and it needs spare parts. Plus, you add mechanical backlash that needs to be compensated for during machine commissioning and every time you have a product changeover—motion and axes synchronization complexity that today’s intelligent drives and servomotors eliminate.
When you strategically locate servomotors as close as possible to the area of motion they are serving, the incremental cost of electric drive components is almost completely offset by eliminating the cost of mechanical components and labor that must be purchased, machined, assembled and configured. In particular, not having to stock multiple sets of sprockets, gears and cams, as well as the time involved in changeovers with mechanical drives, can really drive down the total cost of ownership for the machine.
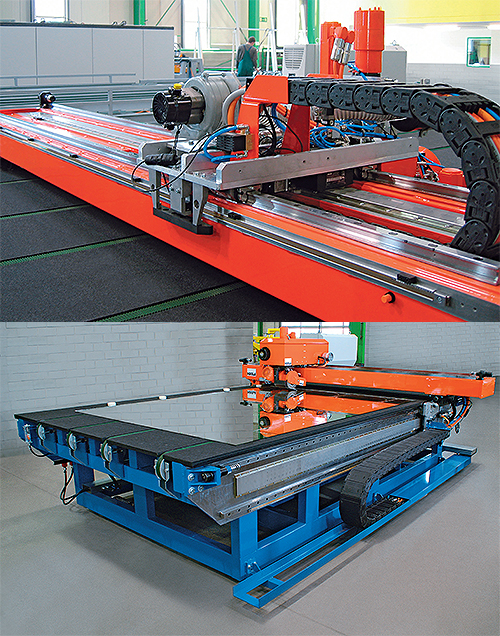
Ultimately, this design approach greatly reduces windup and backlash, improves machine commissioning time, and current state-of-the-art direct drives, direct motors and linear motors allow machine designers to run higher gains and improve the machine’s performance.
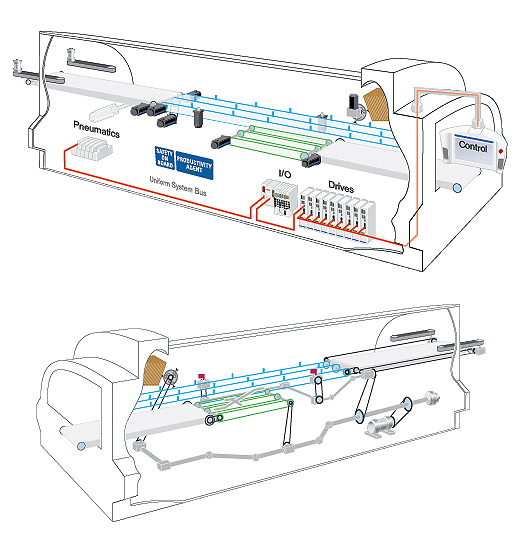
3. Use electronic gearing and camming
Today’s electronic drives and motion control platforms give the mechanical engineer a powerful, flexible tool to improve the accuracy and performance of the machines you design. This technology lets you create a virtual “electronic line shaft” that can electronically synchronize all the drives and motors on the machine, eliminating the mechanical line shaft. In the process, you can dramatically improve axes synchronization and accuracy—from 1/16 or 1/32 in. typical with mechanical line shafts, down to motion precision closer to hundredths or even thousandths of an inch with electronic line shafting.
And this synchronization can be accomplished with zero mechanical backlash—and fewer product jams. It also eliminates a host of mechanical adjustments to bring the machine online, as well as the operator adjustments each time the machine is stopped and restarted.
Electronic gearing and camming makes machine changeover completely programmable. Using FlexProfile technology, with the touch of a button on the HMI screen, you can load a machine recipe, and the changes are made in the control and servo system to run the next product.
This new FlexProfile camming technology makes it possible to build multi-segmented cam profiles based on position, velocity or time-based motion profiles. When you change a section of the electronic cam through a recipe change through the HMI, the control platform will automatically optimize the rest of the cam profile across all of the machine’s motion elements. This enables the machine to run a shorter cycle time, or provide smoother dynamics for the machine, even though a change has occurred, such as a different bag seal time or flap tucking cam position on a cartoning machine.
4. Incorporate energy-efficient technology
One of the fastest growing costs for any manufacturing operation is energy—and good mechatronic design can help control these costs through the application of electric drive and motor systems designed to save energy.
In machines that use servomotors directly coupled to critical axes of motion on the machine, and also use electronic synchronization and camming, the proper sizing of the servo system can create a highly energy-efficient machine.
Proper sizing requires an accurate assessment of several motion factors (motor by motor): how fast the axis needs to accelerate, the size of the mass you’re trying to move, and how precise the acceleration and deceleration needs to be. Undersizing will lead to strains on the drives and motors; oversizing will draw too much power to do too little work.
Some of today’s most cutting edge systems, such as the Rexroth IndraDrive Mi integrated drive/motor systems, include a highly energy-efficient feature: bus sharing. Multiple drives are daisy-chained together and share power from the same bus; in many multi-axis machines, as some motors are accelerating up to speed (drawing power), others are decelerating (regenerating power). With bus sharing, rather than having to deliver maximum power to the accelerating motors and bleed off the decelerating motors into heat across a bleeder resistor, power is shared, so the machine’s power consumption is significantly reduced.
A further energy-efficient technology is called regenerative power supplies. In many machines, multiple servomotors will decelerate at the same time, boosting the voltage to excess levels on the power bus. Older generation electrical drives would bleed that excess electrical energy as heat—wasting the power and adding to the factory floor’s heat production, requiring additional cabinet cooling. With regenerative power supplies coupled to a shared bus system, what was once wasted power can now be fed back through the shared bus and sold back to the electric company.
5. Use HMIs for better troubleshooting
The computer revolution has spread to today’s machine control panel, replacing knobs and pushbuttons with sophisticated PC-based and embedded HMIs with advanced programming and Windows-based operating systems.
Consider your typical office copier: when there’s a paper jam, a touchscreen control indicates where the jam is, what door to open, how to correct the problem, and prompts you what to do next once you’ve cleared the jam. The same user-friendly intelligence is now available to machine designers through today’s touchscreen HMIs featuring the latest graphical user interfaces. Machine layout drawings and schematics can be incorporated into control menus and diagnostic tools, to better manage the machine’s day-to-day operation and troubleshooting ease. Drawings and interactive instructional tools can not only show the precise point where a problem is—they can also show how to open enclosures and what steps an operator can take to put the machine in safe mode for initial maintenance, and other support resources to resolve a problem and step the operator back through the tasks to restart production.
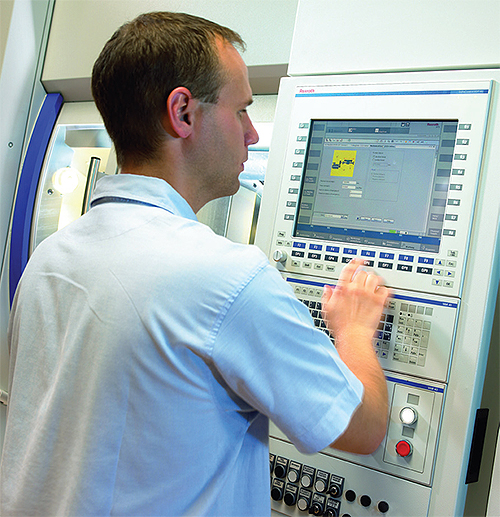

Advanced graphics like this can be combined with the distributed intelligence inherent in servomotor-driven machines, to prevent machine failures or faults before they happen. Called predictive maintenance, this capability lets machine designers set fault tolerance bands in drives and then monitor drive performance. Electric drives and motors, such as IndraDrive systems, allow a broad range of conditions to be monitored—conditions that are directly associated with mechanical performance: variations in load, temperature, vibration, torque, belt tightness and gear meshing are all mechanical events that generate changes in the torque profile of an electric drive and motor moving those machine elements. Mechanical engineers can set tolerance bands for these components, and if they exceed them, then predictive maintenance alerts can be clearly and intelligently displayed over the HMI to operators, along with specific advice about next steps to take to correct the issue before it becomes a serious production problem or something that can damage the machine.
Blending technologies for optimal value
Every electromechanical system should perform its designed function with the minimal use of energy, motion and components required to get the job done—that’s the fundamental goal of any manufacturing engineer. Electrical drive and servomotor systems now offer a wealth of reliable, energy-efficient, digitally intelligent platforms to power the integrated vision of mechatronics to greater value and more innovative manufacturing and automation solutions. Hopefully, the five considerations described here demonstrate the advantages that today’s electric drives and controls offer, helping simplify certain mechanical design and engineering challenges and provide new resources for driving innovation and creativity in machine design.
Bosch Rexroth
www.boschrexroth-us.com


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.