Wiegand sensors are tiny devices that use variations in an external magnetic field to generate electrical signals and energy. They have unique properties that make them a useful option for many proximity sensing systems.
Wiegand sensors are built around small sections of Wiegand wire, a specially prepared ferromagnetic alloy that has a unique physical property. When exposed to an alternating external magnetic field, a Wiegand wire will initially retain its magnetic polarity. However, when the external field reaches a certain threshold, the polarity of the wire segment will abruptly reverse. This polarity switch occurs within a few microseconds and can generate a distinct current pulse in a fine copper coil wrapped around a ferromagnetic core. This pulse is strong enough to activate logic circuits and can be used to energize low power electronic chips. This self-powering capacity of Wiegand sensors helps make them more reliable – and safer – since they can provide signals for alarm systems without external power sources. There’s no need to check or replace backup batteries, sharply reducing maintenance requirements.

Wiegand sensors have been used for proximity sensing in several ways. If the external object is magnetized, or has one or more small permanent magnets mounted on it, then the Wiegand sensor will respond when the object comes close enough to trigger a polarity reversal. This can be used to detect and measure linear or rotary motion. Alternatively, the Wiegand sensor can be mounted between a set of permanent magnets. When an iron or steel object comes close enough, it will have the effect of distorting the magnetic field immediately around the Wiegand sensor enough to trigger a polarity flip and generate a current pulse.
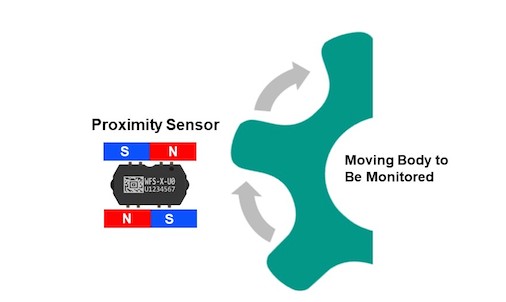
Wiegand sensors offer a number of advantages. For one, they’re intrinsically safe, because their self-powered characteristics mean that they can function without external power sources. There’s also no mechanical contact between the source of the alternating magnetic field and the Wiegand wire assembly and no wear. The sensors are physically rugged and can operate over a wide range of temperatures, and will function reliably for billions of cycles. They’re also insensitive to electrical noise and their response is consistent over a frequency range of near-zero to well over 30 kHz.
POSITAL offers Wigand sensors in package form, consisting of a 15-mm length of Wiegand wire surrounded by a copper coil, all contained in an SMD-mountable plastic support structure.
For more information visit www.posital.com.






Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.