AC motors can be operated directly from AC supply voltage, but this is only suitable if the motor is required to run at constant speed. If the speed or load requirements of the motor change, an AC drive — also referred to as a variable frequency drive (VFD) — can vary the voltage and frequency of power to the motor to control its speed.
What is a Rectifier?
An AC drive is made up of three primary parts: a rectifier, which converts the incoming AC voltage to DC voltage; a DC bus (also referred to as a DC voltage intermediate circuit), which stores the DC power; and an inverter, which converts the DC power back to AC at the necessary frequency and voltage, making it suitable for the motor.
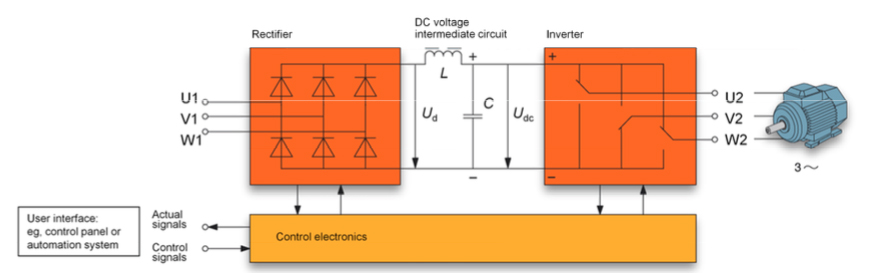
Image credit: ABB Group
The process of rectification results in DC power that consists of pulses of current, so when a device requires steady DC current, the DC bus acts as a low-pass filter and smooths the current.
Types of AC drive rectifiers
The simplest version of an AC drive rectifier is a diode rectifier, which is also referred to as a 6-pulse diode bridge. (Each phase of power requires two rectifiers—one that allows current to pass through when the voltage is negative, and one for when the voltage is positive. Thus, three-phase power requires six rectifiers.)
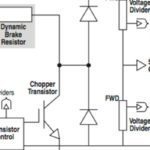
Diode rectifiers are simple and low-cost, but they only allow energy to flow in one direction: from the supply to the motor. So when the motor decelerates and acts as a generator, the regenerated power cannot be fed back into the electrical network—it must be sent to a capacitor via a dynamic braking system.
One alternative that allows for regeneration of power produced by the motor is the thyristor rectifier. Each thyristor bridge uses six thyristors, and bridges are typically applied in pairs. One bridge is used when the motor is consuming electricity (motoring) and the other is used when the motor is generating electricity (regenerating). This allows power to flow in both directions and regenerative power to be fed back to the supply network.
Note that the terms SCR and thyristor are sometimes used synonymously, although SCR is a trade name held by General Electric for a specific type of thyristor.
For regeneration, another alternative is to use an IGBT (insulated-gate bipolar transistor) rectifier. IGBT devices consist of six IGBTs and six diodes, with switching of the IGBTs being controlled by electronics. This allows power to flow in two directions, so energy can be fed back into supply network during regeneration. These rectifiers significantly reduce lower order harmonics. However, they introduce higher order harmonics, so a filter is required, which makes the up-front cost higher for IGBT versions than for other rectifier types. AC drives that use transistors in the rectifier are referred to as having an “active front-end.”
One way to reduce cost in a system with multiple AC motors and drives is to use a single rectifier for multiple devices. The rectifier feeds power to a common DC bus, which is connected to each inverter. Not only does this reduce hardware cost, but it also allows sharing of power between the axes, which increases overall efficiency.
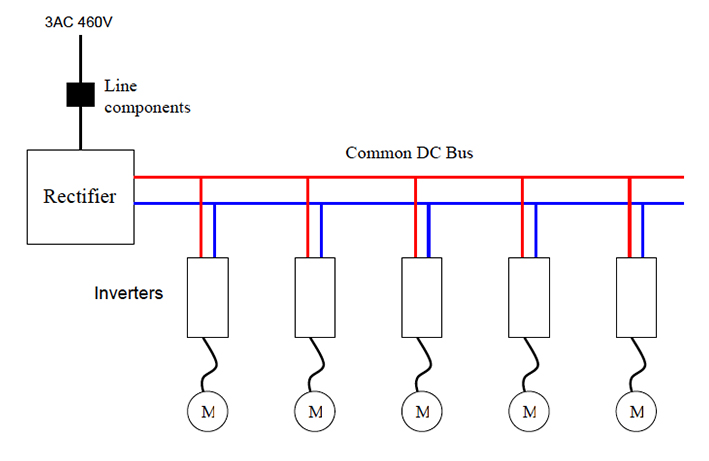
Image credit: Siemens Industry


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.