When a ferromagnetic material is subjected to a mechanical stress — caused by an applied force or torque — it experiences a change in magnetic flux. This phenomenon is known as the magnetoelastic effect, also referred to as the Villari effect, for the Italian physicist who discovered it in the late 1800’s.
In motion control applications, the torque produced by rotating equipment is determined either mathematically, based on the amount of current being drawn (a common method for servo-driven systems) or with the use of strain gauges. But calculated values are not exact representations of real-world results, and strain gauges require precise mounting and calibration to ensure accuracy. A relatively new type of sensor, based on the magnetoelastic effect, is a simple, low-cost technology that uses non-contact sensing to provide accurate torque measurements for rotating or stationary shafts.
The key component in a magnetoelastic sensor is a ferromagnetic ring attached to the shaft being measured. Alternatively, if the shaft is ferromagnetic, a section of the shaft can be permanently magnetized to produce a circumferential magnetic field, eliminating the need for an external ring.
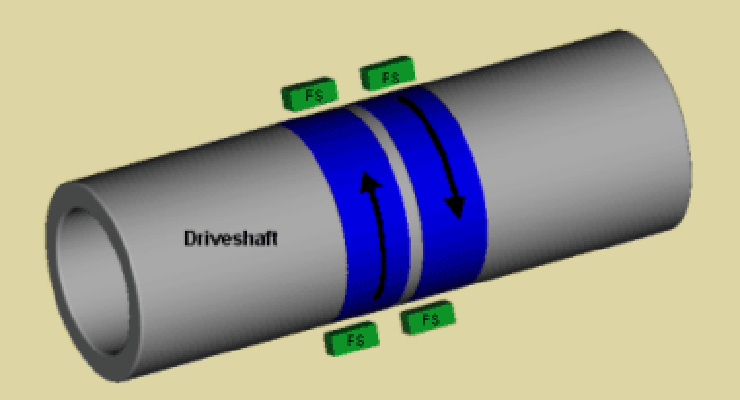
Image credit: MagCanica, Inc.
When torque (torsional stress) is applied, the magnetic moments inside the shaft (or ring) are reoriented, causing a magnetic flux to develop around outside circumference of the shaft. The strength of the magnetic field flux is linearly proportional to the stress — and therefore, the torque — on the shaft, and the polarity of the magnetic field indicates the direction of torque. Magnetic field sensors positioned around the shaft determine the amount and direction of torque based on this flux.
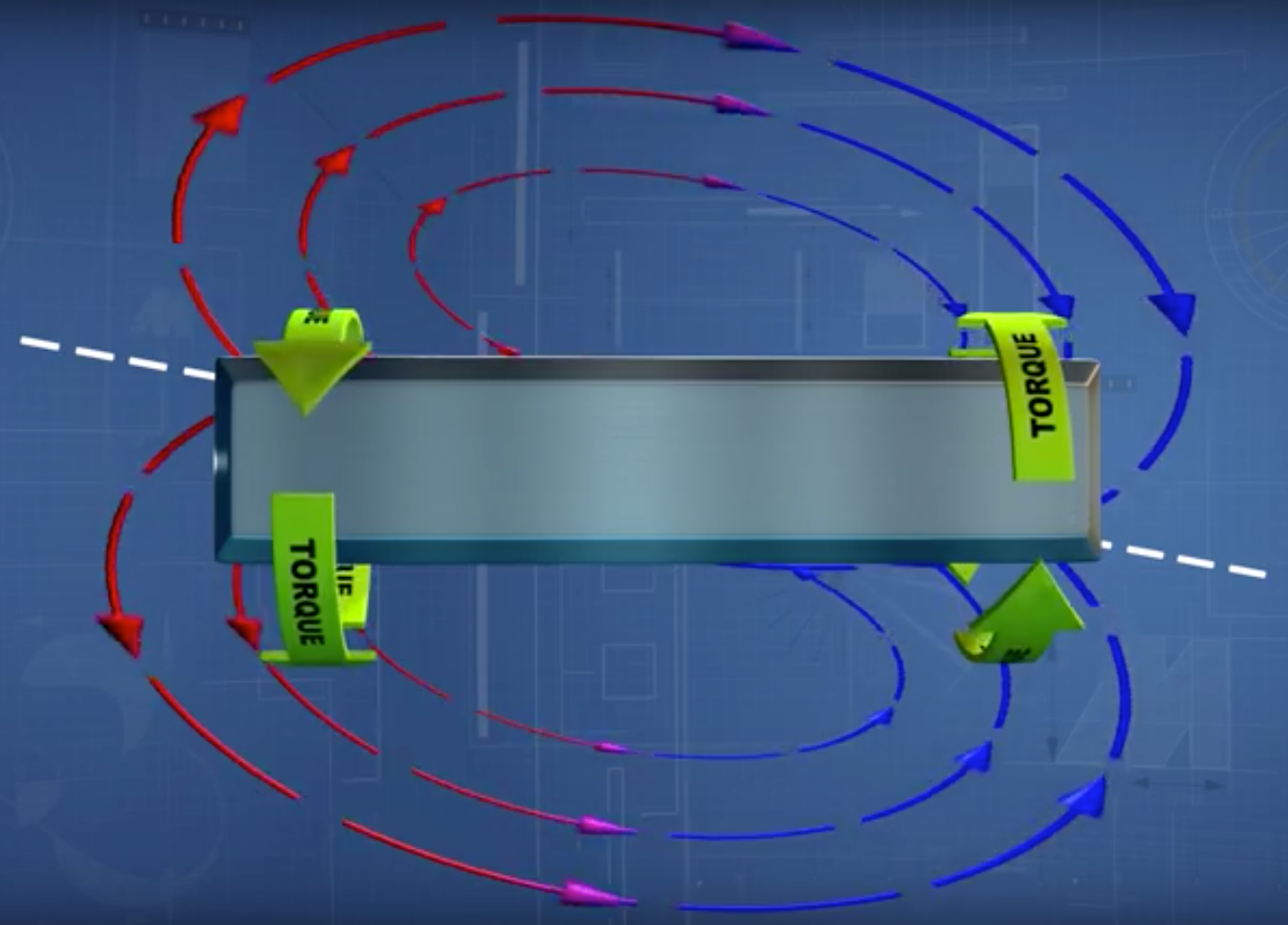
Image credit: Methode Electronics
Magnetoelastic sensors are non-contact, so they don’t suffer from mechanical wear, giving them an extremely long operating life. And because the magnetoelastic properties of a material are highly reliable and don’t degrade, calibration isn’t necessary for sensors that use magnetoelastic technology.
If magnetoelastic sensors seem familiar, it may be because they are similar in function to magnetostrictive sensors. In fact, magnetoelasticity and magnetostriction are essentially inverse effects. Where magnetoelasticity deals with the interaction of magnetic fields and elastic properties of a material, magnetostriction deals with the change in dimensions of a material when a magnetic field is applied.
The most common uses for magnetoelastic torque sensors are in automotive and e-mobility applications, for sensing torque in transmissions and drivetrains. The next areas of growth for this technology are expected to be in the medical robotics and diagnostic equipment markets.

Image credit: BorgWarner
Magnetoelastic sensor technology can also be used to measure linear position, force, speed, or angle.
Despite their widespread use in automotive applications, magnetoelastic sensors haven’t achieved significant adoption in typical motion control applications. This is likely because servo systems, which require precise torque control, are able to quantify torque with sufficient range and accuracy by monitoring the motor’s current draw.
However, large, non-servo controlled motors, such as those used in processing applications and heavy machinery, can benefit from the use of magnetoelastic sensors to monitor torque for predictive and preventive maintenance purposes. Magnetoelastic technology can also be applied to tightening equipment used in assembly and food and beverage applications, where accurate, consistent, torque measurements are important.







Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.