AC motors are commonly paired with variable frequency drives (VFDs), which control motor speed by regulating the frequency of the supplied voltage. Depending on the application and level of speed regulation required, VFDs can be controlled by either scalar or vector methods. The most common type of VFD control is a scalar method referred to as volts per hertz (V/Hz) or volts per frequency (V/f).
The terms variable frequency drive (VFD) and variable speed drive (VSD) are often used interchangeably, but there is a distinction between the two.
A variable speed drive (VSD) is any drive that can control the speed of a piece of equipment, including both AC and DC motors. VSDs can operate via mechanical, hydraulic, or electrical means.
A variable frequency drive (VFD) is used to control the speed of AC motors, and does so by varying the frequency of the supply voltage to the motor.
How V/Hz control works
AC motors are designed for a magnetic field (flux) of constant strength. The magnetic field strength is proportional to the ratio of voltage (V) to frequency (Hz), or V/Hz. But a VFD controls the motor speed by varying the frequency of the applied voltage, according to the synchronous speed equation:
N = 120*f / P
Where:
N = motor speed (RPM)
f = input voltage frequency
P = number of motor poles
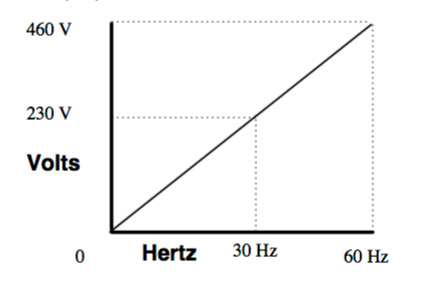
Image credit: Square D
Varying the voltage frequency affects both the motor speed and the strength of the magnetic field. When the frequency is lowered (for slower motor speed), the magnetic field increases, and excessive heat is generated. When the frequency is increased (for higher motor speed), the magnetic field decreases, and lower torque is produced. In order to keep the magnetic flux constant, the V/Hz ratio must remain constant. This keeps torque production stable, regardless of frequency.
V/Hz control of a VFD drive avoids this variation in the magnetic field strength by varying the voltage along with the frequency, in order to maintain a constant V/Hz ratio. The appropriate V/Hz ratio is given by the motor’s rated voltage and frequency. For example, a motor rated for 230 V and 60 Hz will operate best at a V/Hz ratio of 3.83 at all times (230/60 = 3.83).
Traditional V/Hz control does not use feedback, and only changes the voltage and frequency to the motor based on an external speed command. For closed-loop V/Hz control, encoder feedback can be added to measure the motor’s actual speed. An error signal is generated based on the difference between actual speed and commanded speed, and the controller generates a new frequency command to compensate for the error. While it improves speed regulation, closed-loop V/Hz control isn’t common due to the added cost and complexity of the encoder and feedback hardware.
Performance and benefits of V/Hz control
V/Hz control is a simple, low-cost method for controlling variable frequency drives, and is generally regarded as the most common VFD control scheme. It is suitable for both constant torque and variable torque applications and can provide up to 150 percent of the rated torque at zero speed for startup and peak loads. Speed regulation is in the range of 2 to 3 percent of the maximum rated frequency, so this method isn’t suitable for applications where precise speed control is critical. The most common use for V/Hz control is to drive industrial equipment such as fans and blowers.
One unique benefit of V/Hz control over other methods is that it allows more than one motor to be operated by a single VFD. All the motors will start and stop at the same time, and they will all run at the same speed, which is beneficial in some processing applications, such as heating and cooling.
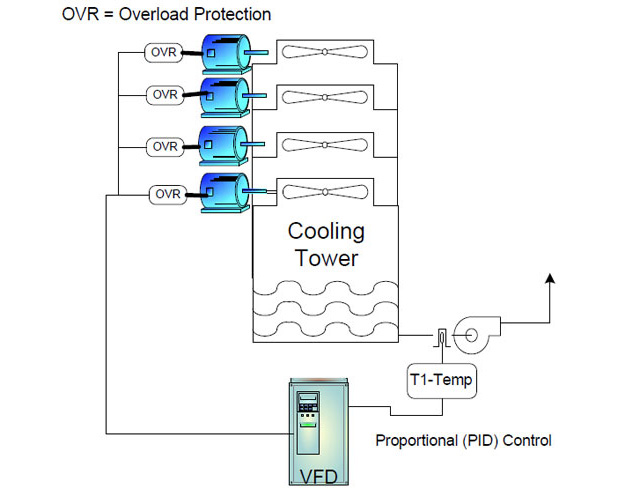
Image credit: variablefrequencydrive.org





Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.