Rotary bearings consist of smooth rollers or metal balls and inner and outer surfaces (races) against which the rollers or balls travel. These rollers or balls carry load carrier and let axes spin freely. Bearings typically encounter radial and axial load. Radial loads are perpendicular to the shaft, and axial loads occur parallel to the shaft. Depending on the application, some bearings must withstand both loads simultaneously.
Here is another batch of articles from motioncontroltips.com Design World sister site bearingtips.com. This site covers rotary bearings that take the form of ball and roller bearings as well as thrust bearings — in addition to the issues of bearing lubrication and integration.
The following are bearing features our colleague Mike Santora has posted there recently. Click on the headlines to read more.
What is a “floating” bearing arrangement?
Two bearings support and locate a shaft axially and radially in relation to the housing, which is stationary. There is “fixed” side and a “floating” side. The fixed side controls the shaft axially. The floating side has more freedom of movement (floating) to help compensate for misalignment and thermal expansion or contraction …
Bearing Lubrication: Oil vs. Grease
Rotary-bearing lubrication takes the form of oil or grease, but grease usually lasts longer, thanks to thickeners that sustain the lubrication layer between raceways and rolling elements. Grease with extreme-pressure additives also extends bearing life when subject to higher forces. Even so, oil is more common for open bearings or those subject to low torque or high speeds. Oils’ lower viscosity imparts less drag than greases …
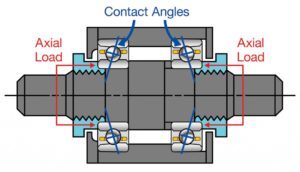 Why is preload necessary in some bearing applications?
Why is preload necessary in some bearing applications?
One of the final steps in the bearing manufacturing process is the assembly of the individual bearing components: the outer ring, inner ring, balls and retainer (or ball separator).
When the bearings are assembled, it is necessary to have a controlled amount of internal clearance, or looseness between the rings and balls … However, in certain applications, this internal clearance must be removed for a pair of bearings to operate properly. The application of an axial load across a pair of bearings for the purpose of removing free internal clearances is preload.
When should oil be used for bearings?
Sean P. Kelly, Field Applications Engineer for NMB Technologies Corporation says that Grease is preferred when longer life is needed.
“This is due to the grease thickener slowly releasing a base oil providing a lubrication layer between the raceways and rolling elements … ”
 Why you should consider air bearings
Why you should consider air bearings
It’s easy to overlook air bearings. Most of the time, mechanical bearings work well enough for a motion application. Most, but not all. Submicron bearing rumble not an option? Is geometric performance and angular repeatability paramount? Here are tips that will smooth out the specification process …
What are minimum loads and why are they important for bearings?
Eric Phaneuf, Applications Engineer, Industrial Market for SKF USA Inc. explains that for many radial bearings, it is common to provide a certain amount of space between the rolling elements and the raceways to allow for thermal expansion and prevent bearing seizure …
What’s being done about counterfeit bearings?
In this interview, Sr. VP, General Council & Secretary for SKF USA Timothy D. Gifford shares some insights into the current counterfeit bearing situation. Specifically, Gifford tells us how the bearing industry is fighting back against the global counterfeiting market …







Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.