Updated 2020 ⚙️ When it comes to gearing components, things can get confusing quickly. There are many terms that gear manufacturers as well as engineers and designers use to talk about what sometimes is essentially the same thing. The term “gearbox” is one of those terms, often times used interchangeably with gearhead or gear reducer … even though they sometimes refer to slightly different physical arrangements of gears.
The most basic definition of a gearbox is that it is a contained gear train, or a mechanical unit or component consisting of a series of integrated gears within a housing. In fact, the name itself defines what it is — a box containing gears. In the most basic sense, a gearbox functions like any system of gears; it alters torque and speed between a driving device like a motor and a load.
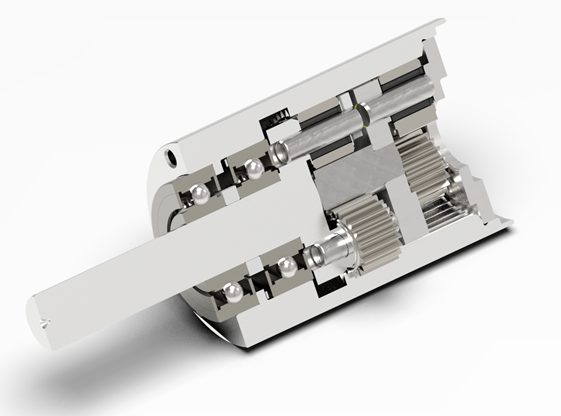
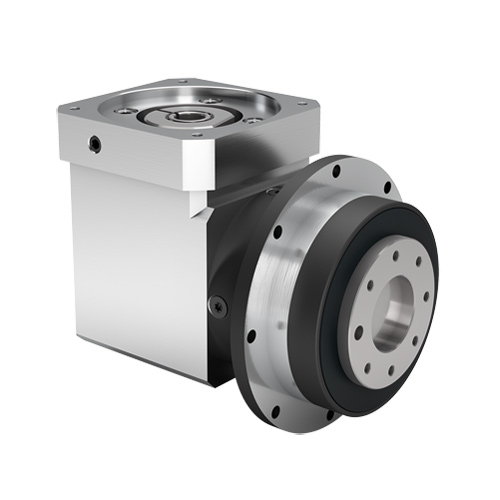

The gears inside of a gearbox can be any one of a number of types from bevel gears and spiral bevel gears to wormgears and others such as planetary gears. The gears are mounted on shafts, which are supported by and rotate via rolling element bearings. The gearbox is a mechanical method of transferring energy from one device to another and is used to increase torque while reducing speed.
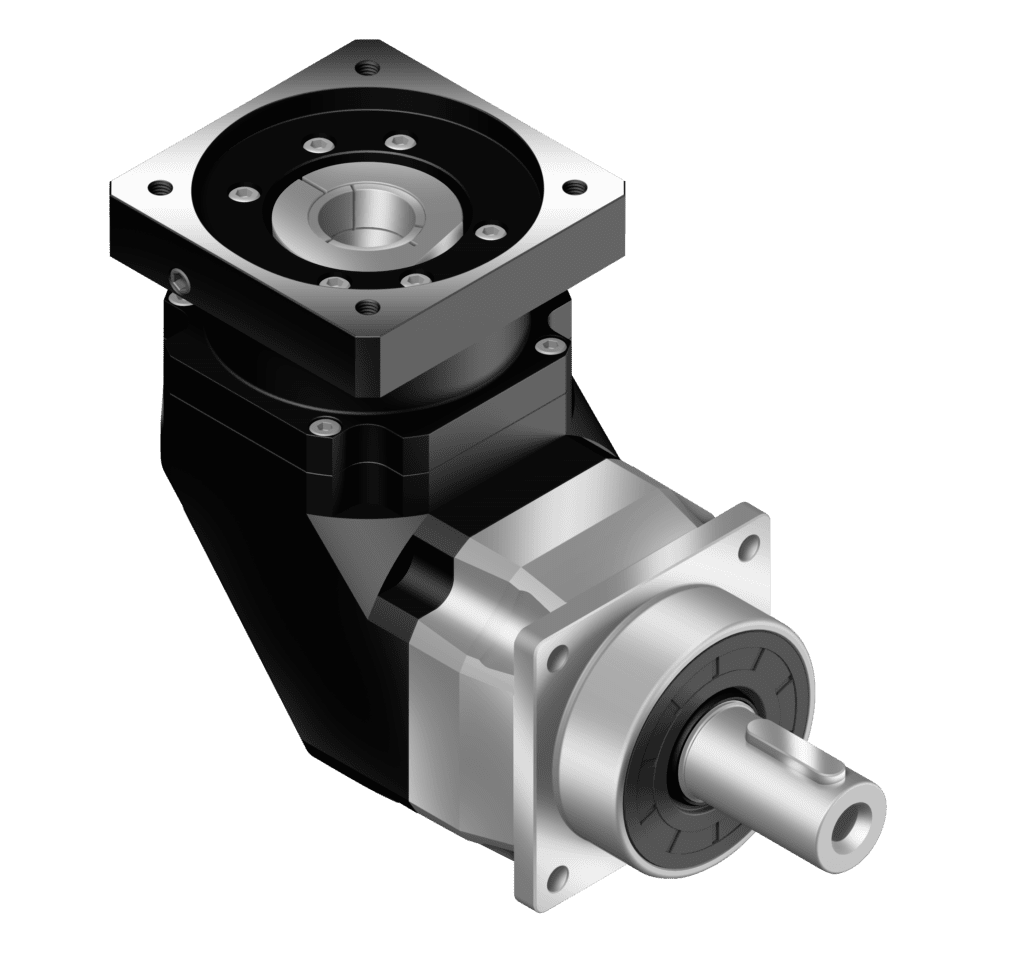
Gearboxes are used in many applications including machine tools, industrial equipment, conveyors, and really any rotary motion power transmission application that requires changes to torque and speed requirements.
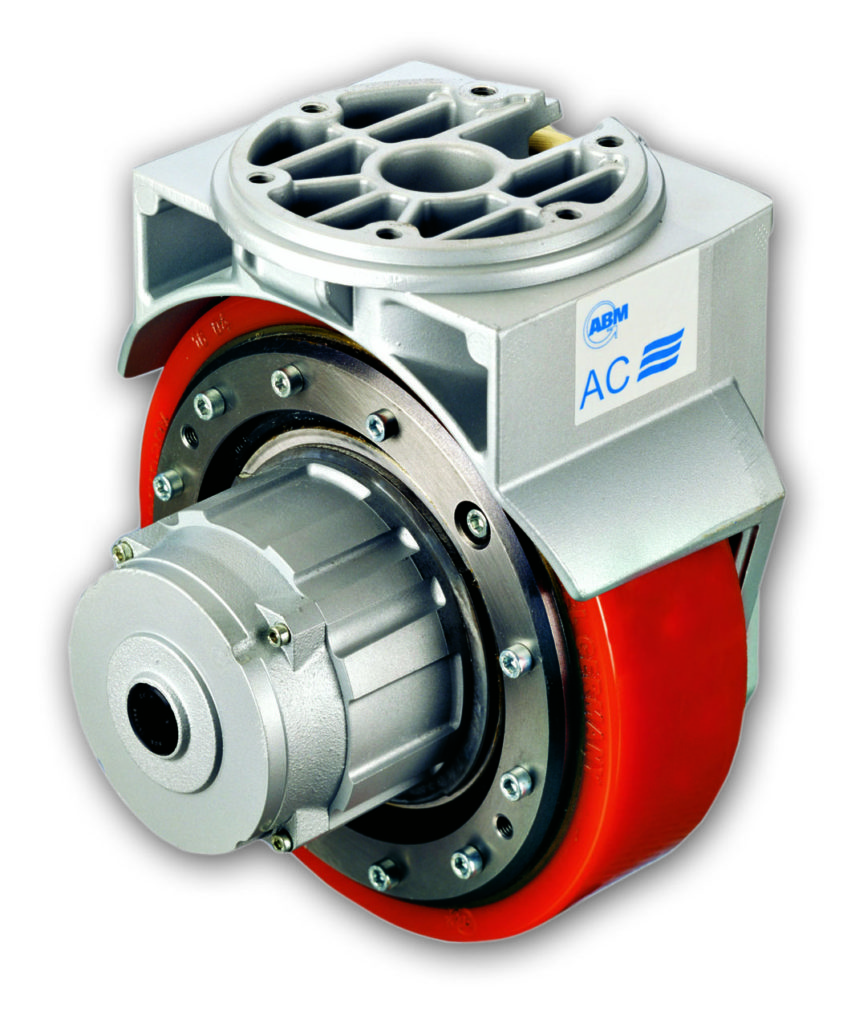

So it’s clear — a gearbox is always a fully integrated mechanical component consisting of a series of mating gears contained in a housing with shafts and bearings (to support and resolve loads) and in many cases a flange for motor mounting. Most of the motion industry makes no differentiation between the terms gearhead and gearbox. But in a few contexts, the term gearbox specifically refers to housed gearing as described above while the more general term gearhead refers to assemblies otherwise open gearing that installs within some existing machine frame. The latter are targeted to compact or battery-powered mobile designs necessitating especially tight integration and omission of extra subcomponents. Here, a series of parallel plates might support the gear-train shafts (and their bearings) and allow bolting to a motor face.
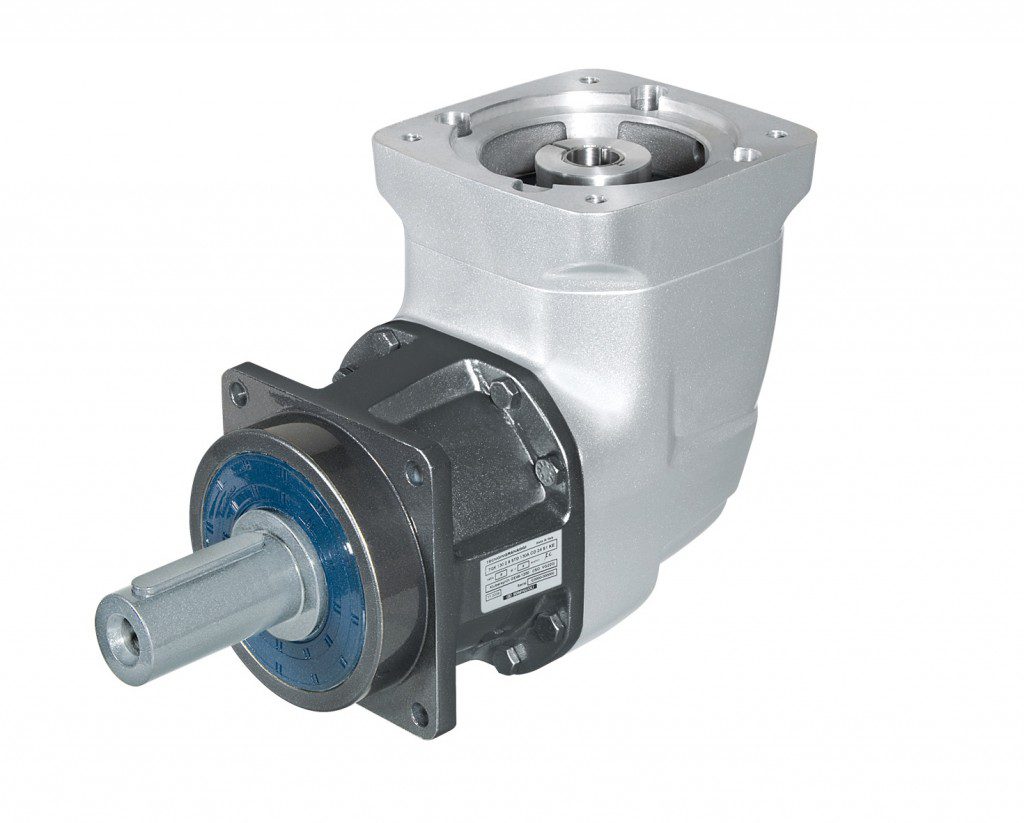

Though beyond the scope of this FAQ, other open gearing simply mounts to the electric-motor output and operates exposed to the environment. Some such open gearing is self-lubricating — constructed of dimensionally stable polyamides or similar materials engineered to meet stringent cleanliness, vibration, weight, and cost requirements. Check out these articles for more information on this topic …
How to Size and Select a Gearbox: A Motion Engineer’s Guide
What are power-transmission gears?






Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.