Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) is a technology that provides Ethernet transmission over a single pair of copper wires, while also transmitting power to connected devices via Power over Data Line (PoDL).
Single Pair Ethernet was initially developed to meet the demands of the automotive industry — smaller, lighter cables and connectors for transmitting data from the numerous sensors involved in adaptive cruise control, parking-assist, autonomous driving, and other onboard systems. In fact, the lower data loads and shorter distances required in automotive applications were the perfect fit for early SPE developments.
But as the technology evolved, companies began seeing its potential in other applications — especially manufacturing and building automation — and the SPE Industrial Partner Network was developed. This association of manufacturers promotes Single Pair Ethernet as the “basis for establishing the IIoT” and also supports standards for transmission protocols, cabling, and device components.
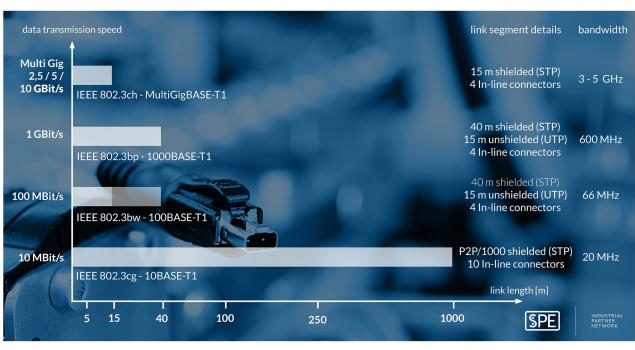
Image credit: SPE Industrial Partner Network
Traditional Ethernet requires two pairs of wires for data transmission rates of 100 Mbps, or four pairs of wires for 1 Gbps transmission rates. Single Pair Ethernet uses just one pair of wires to transmit data at rates of 1 Gbps for distances up to 40 m, or at 10 Mbps up to 1000 m — offering a significant reduction in cable size, cost, and complexity. And although traditional Ethernet has been implemented all along the automation pyramid, devices at the lowest level — the field level — are still often controlled by fieldbus protocols. SPE offers an Ethernet solution that can be implemented at all levels — from the cloud to the field — eliminating the need for gateways and other hardware that are required for various networks to “talk” to each other.
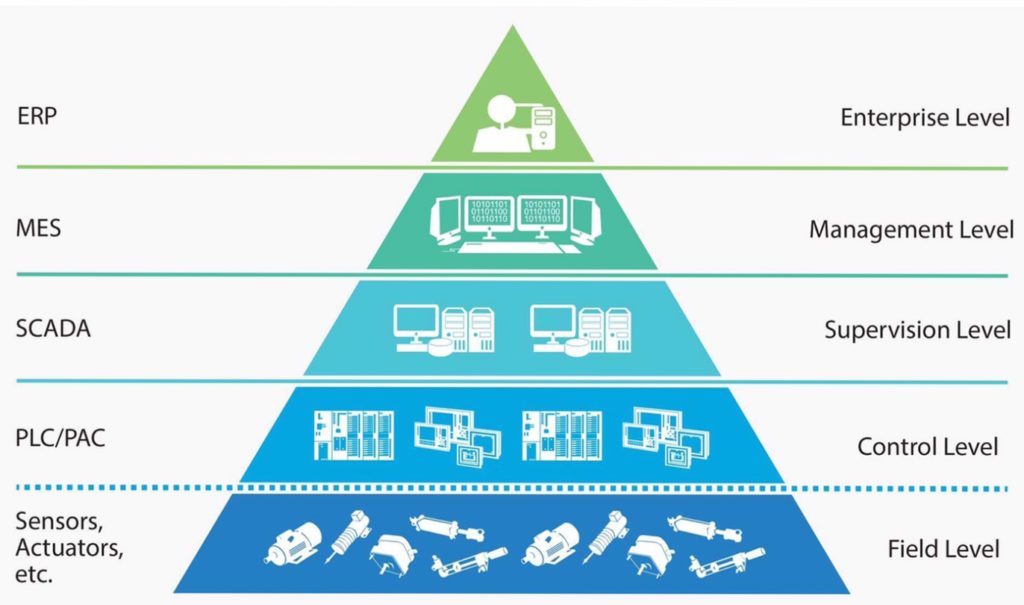
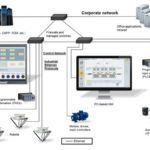
Image credit: MIAC Automation
Smaller cables also use smaller connectors — another benefit of SPE in space-constrained applications or those with numerous, small devices at the field level. And the smaller bend radius of a thinner cable makes installation, routing, and management less cumbersome and more flexible, both literally and figuratively.
With the ability to transmit power — up to 50 W — together with data, SPE is positioned to be an ideal solution for IIoT applications, in which many field-level devices require power along with fast, real-time communication to higher-level controls or to the cloud. And for applications that require more than 50 W of power, hybrid solutions using four conductors are available, taking power capabilities up to 96 W at 24 V or 392 W at 48 V.
How does SPE achieve fast Ethernet communication with just one pair of wires when traditional Ethernet requires four pairs?
Classic 1 Gbps Ethernet uses a Cat 5 cable with four pairs of wires and operates at frequencies up to 100 MHz. Each pair can send and receive data, allowing transmission rates up to 1 Gbps. Single Pair Ethernet uses just one pair of wires, but operates at frequencies up to 600 MHz. In this wide frequency band, some frequencies send data and others receive data, enabling 1 Gbps transmission speeds with just one pair of wires.



Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.