Here we answer the common question: What do the technical terms conductivity, electrostatic dissipation and coefficient of friction mean? Then they relate these values to engineered designs that have rubbing parts that necessitate some way to address static-electricity buildup.
What are conductivity and electrostatic dissipation?
Conductivity is a measure of the ability of a material to conduct electrical current.
Consider this value in the context of motion design such as an ATM or other high-speed piece of equipment that takes currency and documents through a machine. Such motion can lead to a buildup of static electricity …
… and this static charge must be managed to prevent critical malfunction, equipment damage and even the chance of a fire.
Here, some urethane elastomers are formulated to be semi-conductive within a prescribed range of conductivity to dissipate harmful static electricity buildup.
MPC makes parts that are formulated to be semi-conductive by modifying the urethane structure at the molecular level, avoiding the use of carbon black or conductive particles, which can shed and cause equipment short circuits as well as marking the currency or documents with a black smear.
What is COF or coefficient of friction?
Coefficient of friction or COF is the resistance to motion between two contacting surfaces. COF is an important consideration in currency-document handling machines for controlling the grip of a belt, wheel or roller against various types of currency, paper, tickets or cards. Consistent COF enables a part to grab one item at a time, move it a precise distance, and let go at exactly the right moment.
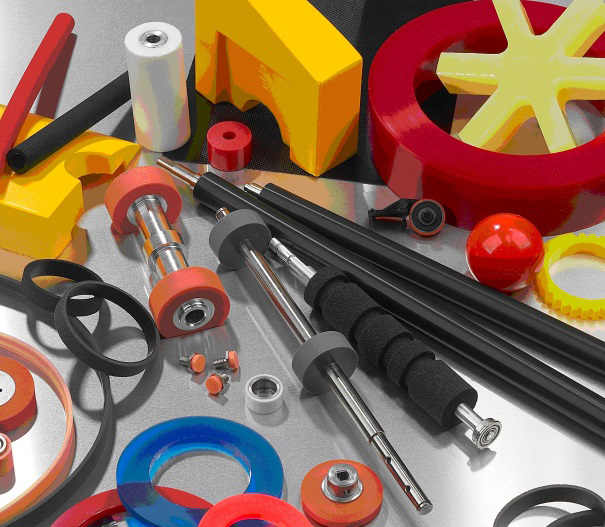

These methods ensure a consistent COF over a long period of time, ensuring long, trouble-free performance. MPC’s materials also prevent clogging and glazing of the contact surface, which is frequently a cause of equipment failure with other materials. Thank you to engineers from Mearthane Products Corporation (MPC) — a manufacturer of parts of thermoset polyurethanes — for helping to answer these common questions.





Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.