The EC-i 52-mm motor is one from a family of EC brushless dc motors from maxon. It’s an iron-wound internal rotor motor redesigned from 7 pole pairs to 8 pole pairs. This significantly reduces the vibration and noise output of the dc motor. Available in three voltage outputs, 18, 24 and 48 V, the 52-mm […]
DC Motors
Slotless brushless motor designs offer three advantages: Details on linear behavior and more
In a recent video recorded at the Design World studios, I teamed up with my colleague Paul Heney to review the features of three motors (including slotless brushless motor options) from Koford Engineering in Winchester, Ohio. Related article: What are the differences between slotted and slotless motors? Brushless motors are like brush motors but use electronic […]
New brushless dc motor with integrated drive from Allied Motion
Allied Motion Technologies’ new KinetiMax 42 EB is a 42-mm diameter outer rotor, brushless dc motor with an integrated drive. Extremely compact, the KinetiMax 42 has a robust bearing system capable of handling high side loads and a minimum operating life of 20,000 hours. The KinetiMax has an integrated speed control loop with speed set […]
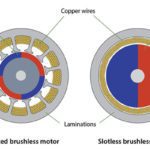
What are the differences between slotted and slotless motors?
The original brushless DC (BLDC) motors were designed with slotted stators, and the majority of BLDC motors are still made this way. But this design produces cogging torque, which makes it difficult to achieve smooth motion, especially at slow speeds. To eliminate this effect, a new design was developed, eliminating the slots in the stator (which […]
Oriental Motor launches new website at orientalmotor.com
Oriental Motor’s new website at orientalmotor.com is now easier than ever to use with the simplicity of the previous site but with more information and better tools. So now, design engineers can find and select the right motor for their motion designs more easily than before. More specifically, engineers can use a sizing tool to […]
Why use brushed servo motors?
The idea of brushed servo motors may seem a bit counterintuitive—most of us think of servo motors as high-performance devices used in highly dynamic applications, while brushed DC motors are low-cost solutions for mass-produced consumer devices. And, to a large extent, this is correct. But remember that “servo motor” is a fairly broad term that […]
Trends in electric motors part one: Market shifts towards smart solutions
This year in motor design there’s been an uptick in three trends. Disposable medical devices, new consumer products, and the automation of humbler tasks are driving demand for affordable and miniature-motor options. (Read more about motor miniaturization in the second installment of this two-part Motion Trends series on electric motors here.) A related trend towards […]
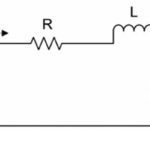
FAQ: What’s the difference between torque constant, back EMF constant, and motor constant?
A DC motor’s output torque is directly proportional to the current through the windings, and the motor’s angular speed is directly proportional to the back EMF that it generates. These simple relationships are typically given by the equations: Where: T = torque (Nm) I = current (A) kT = torque constant (Nm/A) And Where: ω = […]
Oriental Motor releases brushless dc motor with high-gear-ratio gearheads
Oriental Motor now sells new options from its BMU Series — two new high-strength and high gear ratio gearheads … … the foot-mount JB Gear and the flange mount JV Gear joining the right-angle hollow shaft JH Gear. These new gearheads work with the company’s 200 Watt (1/4 HP) or 400 Watt (1/2 HP) BMU Series brushless DC motors. […]
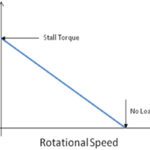
The Torque Equation and the Relationship with DC Motors
Understanding the torque equation and the relationship between speed and torque is an important part of selecting and operating a DC motor. DC motors are relatively simple machines: when the load on the motor is constant, speed is proportional to supply voltage. And when supply voltage is constant, speed is inversely proportional to the load […]