Of the three primary stepper motor designs — permanent magnet, variable reluctance, and hybrid — hybrid stepper motors are arguably the most popular in industrial applications, combining the best performance characteristics of permanent magnet and variable reluctance types.
Hybrid stepper motors are constructed with a rotor made of two sections, or cups, with a permanent magnet between them. This causes the cups to be magnetized axially — with one cup polarized north and the other cup polarized south. The surfaces of the rotor cups have precisely-ground teeth (typically 50 or 100 teeth per cup), and the cups are aligned with an offset of ½ tooth pitch between the two sets of teeth.
In a hybrid stepper motor, the stator poles are also toothed, and when pulses are delivered to the stator by the stepper drive, these poles are magnetized, causing the rotor to turn so that the teeth of the rotor and stator align (N-S or S-N).
This hybrid design — with teeth on both the rotor and stator — allows the motor to optimize magnetic flux, and therefore, produce higher torque than permanent magnet or variable reluctance designs. Hybrid stepper motors can also achieve step angles as small as 0.72 degrees in full-step mode and operate at higher speeds than other designs.
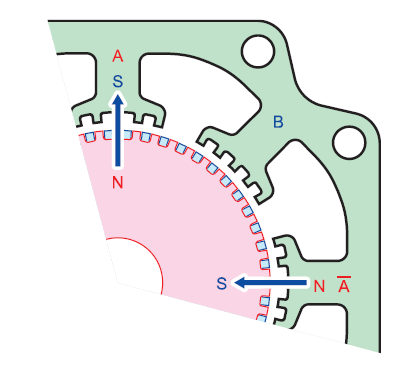
Image credit: Oriental Motor
Although proprietary designs and production methods allow manufacturers to optimize the torque output (as well as step accuracy and speed characteristics) of their hybrid stepper motors, torque production is still closely tied to the frame size of the motor.
Stepper motors generally adhere to the NEMA ICS 16-2001 standard for frame sizes, which specifies mounting dimensions such as flange size and bolt circle diameter. However, one dimension not covered by the NEMA standard is motor length. And this flexibility in motor length for a given frame size provides manufacturers with another option for increasing the torque production of a particular NEMA size stepper motor — by creating motors with longer stack lengths. For example, double- and triple-stack stepper motors are now common offerings from several manufacturers.
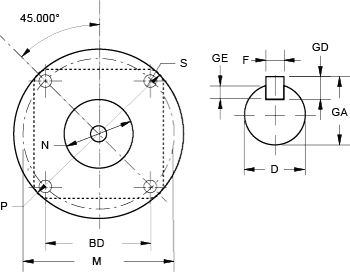
Image credit: Schneider Electric Motion
Double- and triple-stack hybrid stepper motors simply have multiple rotors and stators, stacked end-to-end. With multiple rotor and stator sections, the motor can produce more torque without the need to increase the frame size. Only the length of the motor increases. (Note that a few manufacturers also produce quad-stack stepper motors, as shown below.)

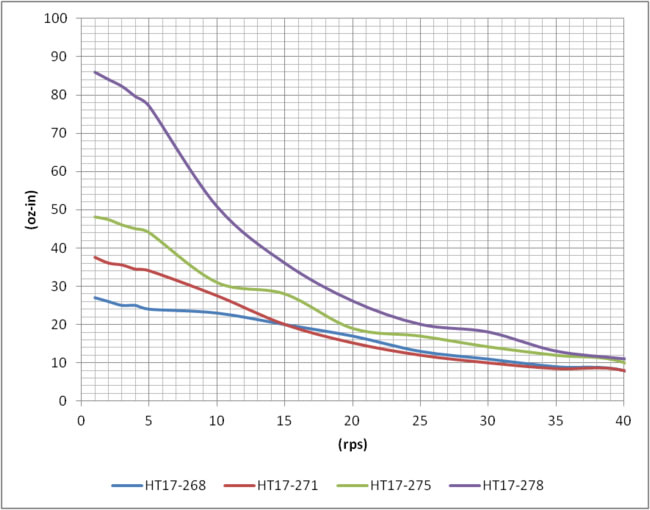
Image credit: Applied Motion Products
However in double- and triple-stack (and quad-stack) stepper motor designs, torque falls off faster as speed increases than it does in single-stack designs. This is because the added rotor and stator sections also increase the motor’s inductance. And higher inductance means the electrical time constant of the motor — the amount of time it takes the current in the windings to reach 63 percent of its maximum value — is also increased. When a stepper motor operates at high speeds, a high electrical time constant means there isn’t enough time for the current (and, therefore, torque) to reach its maximum value at each motor step, resulting in a torque drop-off as speed increases.
Another way to increase the torque from a stepper motor — without increasing the NEMA frame size — is to use a gearbox with the motor. The addition of a gearbox not only increases the torque delivered from the motor to the load, it can also provide better inertia matching between the motor and the load. And when connected to a gearbox, the motor can operate at higher speeds, which helps reduce or avoid resonance and oscillations.





Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.