Resolvers and encoders are both devices that measure the rotary position of a shaft by converting mechanical motion into an electrical signal. Resolvers have a longer history, originally used in military applications and adopted for industrial use due to their rugged design. But encoders are taking the place of resolvers in many applications. What’s driving the shift […]
FAQ: What do X1, X2, and X4 position encoding mean for incremental encoders?
An encoder is a device that measures position, and in some configurations, can also measure direction. Rotary encoders measure rotation of a shaft, while linear encoders measure distance traveled. For both types of encoder, the position measurement can be either incremental or absolute. An incremental encoder measures change in position, but does not keep track of […]
Linear encoder types — and parameters for selection
Linear encoders monitor linear movement and provide position feedback in the form of electrical signals. In servo driven systems, linear encoders supply the precise position of the load, typically in addition to the speed and direction feedback provided by the motor’s rotary encoder. For stepper driven systems, which typically operate in open-loop mode with no position […]
FAQ: Do piezo motors have any holding force when de-energized?
There are two forces in piezo motor operation that are often confused: stall force and holding force. The stall force is the maximum force a motor can hold while running (i.e. in a dynamic state) before stalling occurs, while the holding force is the maximum load a motor can hold while powered-down (i.e. in a static […]
FAQ: What benefits do piezo motors offer?
Piezo motors rely on piezo materials, which are ceramics that change shape when an electrical field is applied, to produce vibrations that cause motion—either linear or rotary. (Conversely, piezo materials can also produce electricity when mechanically loaded.) There are several principles on which piezo motors can operate, with the most common of these being the use of ultrasonic […]
What’s the difference between servo and closed-loop stepper motors?
Servo and stepper motors have similar construction and share the same fundamental operating principle. Both motor types incorporate a rotor with permanent magnets and a stator with coiled windings … and both are operated by energizing or applying a dc voltage to the stator windings, which then causes the rotor to move. However, this is […]
FAQ: What is servo motor inertia and why does it matter?
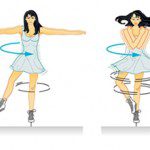
Inertia is an object’s resistance to a change in speed. To determine the inertia of an object, its mass is multiplied by the square of its distance from the axis of rotation. A familiar demonstration of inertia is a figure skater on the ice. When she spins with her arms close to her body, her mass […]