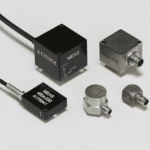
Condition monitoring of machines is intimately linked with the larger program of predictive maintenance. The goal of predictive maintenance is to reduce or eliminate entirely sudden and catastrophic machine failure by actively monitoring those components that are critical to machine function. By monitoring components such as motors, fans, pumps and other constituent components such as […]
FAQs + basics
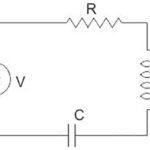
What’s the difference between resistance, reactance, and impedance?
DC circuits are relatively easy to analyze, due to current flowing in one direction, with resistance being the main element of the circuit. AC circuits, on the other hand, are more complex, since voltage and current alternate direction with a given frequency. Whereas DC circuits have resistance, AC circuits often have resistance and another property, known […]
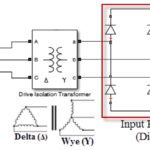
What are drive isolation transformers and how do they differ from line reactors?
A variable frequency drive alters the speed of an AC induction motor by rectifying incoming AC power to DC, storing the DC power in a bus, and then converting the DC power back to AC at the voltage and frequency required to meet the load demands. Although this matching of the motor speed to the […]
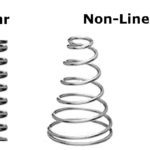
What are linear springs and how do they work?
Springs that follow Hooke’s Law are often referred to as “linear springs” because they have a linear relationship between load and deflection. A linear spring has the same diameter along its entire length, and this uniform diameter gives it a constant spring rate. In other words, the spring rate doesn’t change regardless of the load acting on […]
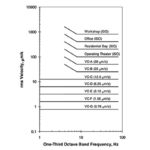
What are vibration criteria and VC curves?
Precision manufacturing and testing processes are highly sensitive to vibrations, which often result from both internal sources such as foot traffic, fans, and pumps, and external ambient sources such as outside traffic, construction, and other nearby industrial activities. To address these concerns, a set of “generic” vibration criteria was created in the 1980s by Eric Ungar […]
August 2020 Motion Systems Handbook
View the full issue by clicking below: Commentary Terminology: A modest proposal The time has come. In fact, I’d say that it’s long past due. Just what exactly am I talking about? I’m talking about some common terminology used in the software, industrial controls and IT worlds, specifically two words that refer to control and […]
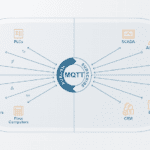
What is MQTT and when is it used in motion applications?
Message queuing telemetry transport — commonly referred to as MQTT — is a machine-to-machine (M2M) messaging protocol that is extremely well-suited for devices that have low or unreliable network bandwidth. Although it was originally developed in the late 1990s for the oil and gas industry to address equipment in remote locations, MQTT has been an […]
What are power factor correction capacitors?
The measure of how efficiently a piece of equipment or facility uses power to produce work is known as its power factor. Although resistive loads, such as heating and lighting, have a high power factor, inductive loads, including AC induction motors, don’t use all of their supplied power to produce useful work, so their power […]
What is flux braking and how does it differ from regenerative braking?
AC induction motors are used to drive loads such as fans, pumps, lifts, and conveyors. But in some applications, the motor is also used as a brake to stop the load, reverse its direction, or hold the load and prevent it from moving. And while there are several methods of braking for AC motors, if […]
What role does Linux play in motion control systems?
Operating systems manage the communication between hardware and software in devices such as servers, computers, mobile phones, and embedded systems. Most personal computers and laptops use either Microsoft’s Windows operating system or Apple’s macOS, and mobile devices such as phones and tablets primarily use Google’s Android operating system or Apple’s iOS. In the industrial world, […]