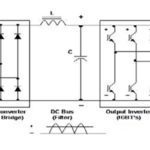
Despite the benefits of using medium voltage AC drives for high horsepower motors, low voltage technology holds a dominant place in the AC drive market, for both low- and high-power applications. There are multiple reasons for this, not the least of which are cost and availability. Medium voltage drives have historically been custom-engineered solutions, with low-volume production, […]
AC Motors
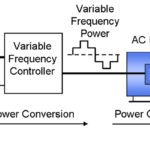
FAQ: What are medium voltage AC drives, and where are they used?
Recall that the basic equation for electric power is P = VI, or, power = voltage multiplied by current. This means that for a given power level, voltage and current are inversely proportional. In other words, the higher the supply voltage, the lower the current draw will be. For AC motors that are used in high-power applications, […]
Lafert high-performance standalone (HPS) permanent-magnet ac motors boost design efficiency
HPS Series permanent magnet (PM) synchronous ac motors from Lafert North America deliver IE4 Super Premium energy efficiency while reducing motor size and weight by 50% in some cases. HPS Series motors combine the mechanical design of standard induction motors with the performance and efficiency of brushless servo motors. The TEFC motor design results from decades of […]
FAQ: How do drives affect cogging in AC motors?
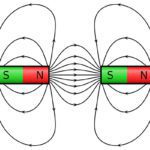
If you put two magnets in close proximity to each other, you know that they’ll experience an attractive force when opposite poles are near each other and a repulsive force when like poles are near. If you hold one magnet stationary and rotate the other, pole-over-pole, the rotating magnet will tend to stop when its […]
AutomationDirect adds more premium efficiency IronHorse AC motors
AutomationDirect’s IronHorse line of general-purpose three-phase motors now includes the MTRP-series 56HC-frame premium efficiency motors available from 1 to 3 hp. The rolled steel motors are available in 1,800 and 3,600 rpm models and feature 4:1 constant torque and 10:1 variable torque speed ranges, TEFC frames, cast aluminum end bells and removable mounting bases. MTRP-series […]
How to use servo drives with asynchronous (induction) motors?
With high construction costs of rare earth permanent magnet synchronous servo motors, asynchronous (induction) motors are more acceptable, when possible. By Craig Dahlquist • Application Engineer at Lenze Americas One way to get servo control of an asynchronous motor (on 400 to 480 Vac supply voltage) is to use a conventional 230/400 or 230/460 Vac (delta/wye connection) […]
FAQ: When to use a DC drive vs an AC flux-vector drive
DC drives are known for their ability to provide tight speed control and full torque at any speed, whereas traditional AC drives had a more narrow speed range and limited torque control. But newer AC drives using vector control, also known as field oriented control (FOC), have performance similar to DC motor and drive systems. Through […]
FAQ: What are current source inverters and voltage source inverters?
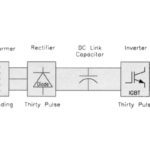
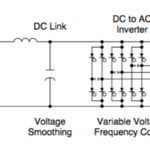
As we’ve discussed before, the main components of a variable frequency drive (VFD) are a rectifier (also referred to as a converter), which converts AC voltage to DC voltage, a DC bus (also referred to as a DC link), which filters and stores the DC power, and an inverter, which converts the DC power back to […]
FAQ: How does EU Regulation 428/2009 apply to AC drives?
AC drives capable of operating at frequencies of 600 Hz or greater are generally referred to as “high-frequency” drives. These drives are considered by the U.S. and the EU to be dual-use devices, meaning that although they are commonly used in civilian applications, such as industrial equipment, they can also be used in military applications or […]
What are VFD reflected waves and why are they harmful?
Reflected waves, also known as transmission line effects or standing waves, are over-voltages that can damage the motor and cable. The use of IGBTs (insulated gate bipolar transistors) in variable frequency drives has helped to improve VFD performance in several ways. First, their quick switching time (also referred to as rise time, or dV/dt) means […]