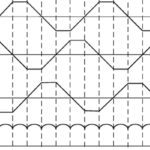
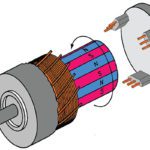
In a brushless DC (BLDC) motor, permanent magnets are mounted to the rotor, and the stator has windings that are energized by external current to produce electromagnetic poles. Brushless motors use electrical commutation to determine the switching sequence of the stator coils, and BLDC motors can be driven with either trapezoidal or sinusoidal commutation. Trapezoidal commutation is […]
What is TTL output for incremental encoders?
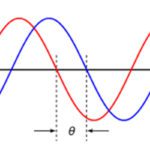
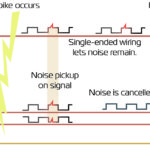
Updated August 2018 || Rotary encoders are used to track the angular position of a shaft, providing either incremental or absolute position information. Incremental rotary encoders work by generating pulses as the shaft rotates. By counting the number of pulses, the position of the shaft relative to its starting position can be determined. Rotary encoders […]
FAQ: How do drives affect cogging in AC motors?
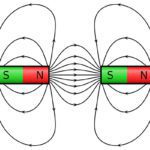
If you put two magnets in close proximity to each other, you know that they’ll experience an attractive force when opposite poles are near each other and a repulsive force when like poles are near. If you hold one magnet stationary and rotate the other, pole-over-pole, the rotating magnet will tend to stop when its […]
FAQ: What are ways to avoid torque ripple in DC motors?
Torque ripple—variations in torque production during shaft revolution—is an undesirable effect that occurs in permanent magnet motors, preventing smooth motor rotation. Torque ripple is generally defined as non-linear torque production of an energized motor. Cogging torque—a phenomenon similar to torque ripple—is torque produced by the attraction between the permanent magnets of the rotor and the […]
What are typical drive-based safety functions?
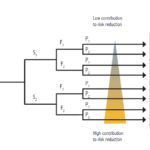
Functional safety standards EN/IEC 62061 and EN/ISO 13849-1 ensure safety via electronic solutions, unlike traditional safety systems, which used electromechanical components to achieve safety. And while functional safety applies to a machine and its control system (not to individual components), the drive lies at the heart of the safety implementation. In fact, functional safety specifies that […]
What are functional safety standards for servo drives?
Safety is a serious concern for machine builders, system integrators, and end users. Not only do they have a responsibility to provide a safe production environment, they must also meet regulatory requirements for machine safety. And of course, all of this should occur with minimal impact on operational efficiency and productivity. Fortunately, functional safety features […]
FAQ: What are Hall effect sensors and what is their role in DC motors?
DC motors can be either brushed type, which are mechanically commutated, or brushless, which are commutated electrically. In brushless DC (BLDC) motors, Hall effect sensors are used in place of a mechanical commutator and brushes. Hall effect sensors are solid-state, magnetic field sensors. They work on the principle that when a conductor with current flowing through […]
FAQ: Can DC motors run at lower than nominal voltage?
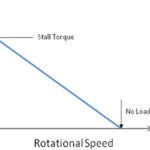
In a DC motor, the relationships between voltage and speed and between current and torque are straightforward. When the load (torque) on the motor is constant, speed is proportional to the supply voltage. And when the supply voltage is constant, speed is inversely proportional to the load (torque) on the motor. Specifications for DC motors include […]
FAQ: What are PID gains and feed-forward gains?
Gain is the ratio of output to input—a measure of the amplification of the input signal. A common example is the volume button on a stereo. This button controls the ratio of the input signal (received from the radio station) to the output signal (how loud the sound is from your speakers). When the volume is […]
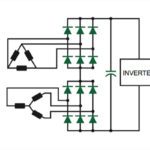
FAQ: What is a pulse rectifier and what kinds are there?
Variable frequency drives are made up of three primary sections: a rectifier, which converts the supplied AC voltage to DC; a DC bus, which stores the DC voltage; and an inverter, which converts the DC power back to AC at the voltage and frequency required by the motor. The most common, and simplest, rectifier designs use […]